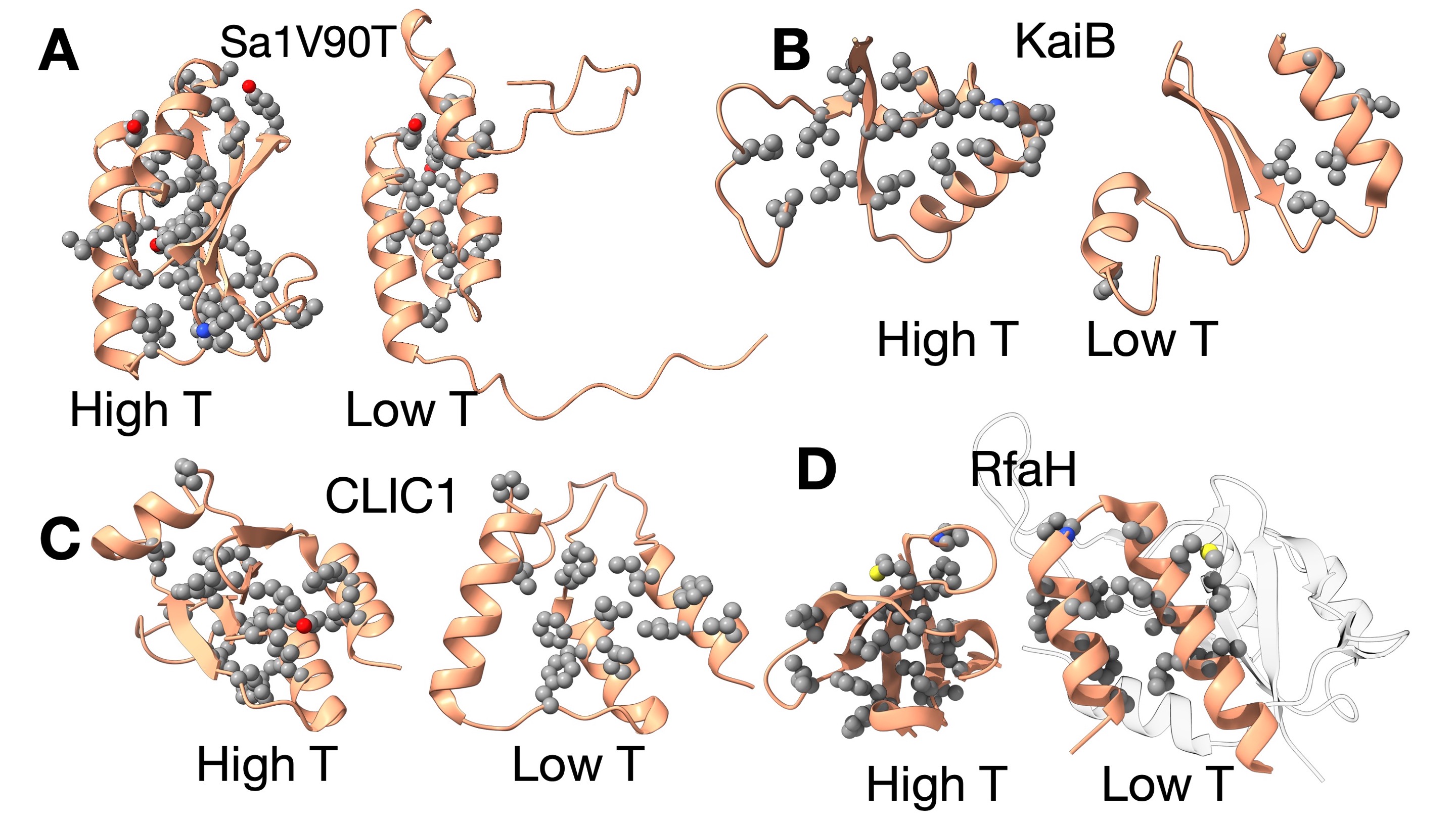
New Study Uncovers Temperature-Driven Mechanism in Metamorphic Proteins
Dr. John Orban, IBBR Fellow and a Professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at University of Maryland and his co-author Andy LiWang, a Professor of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of California, Merced, recently published a Perspectives article “Unveiling the cold reality of metamorphic proteins” in PNAS...
.png)
Structural Biology Day at IBBR
The Institute for Bioscience and Biotechnology Research (IBBR) invites you to participate in our second biennial Structural Biology Day on Wednesday, May 7, 2025 at our facility in Rockville, Maryland. The event will feature research talks in various aspects of structural biology, including cryoelectron microscopy, X-ray crystallography, mass spectrometry, diffraction...
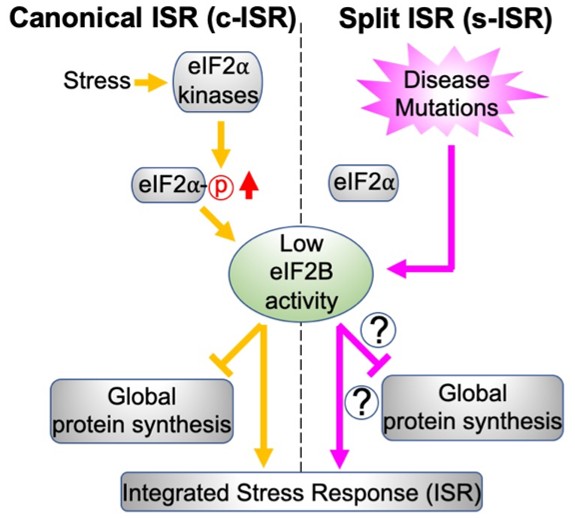
Uncovering the Split ISR Pathway: A New Understanding of Cellular Stress and Its Implications for Treating Genetic Diseases
A recent study has challenged the long-standing understanding of how our cells respond to stress. For decades, scientists believed that cells react to various stressors—such as starvation, infection by pathogens, heat, and iron deficiency—through a unified pathway known as the Integrated Stress Response (ISR). The ISR functions by modulating protein...
About IBBR
IBBR is a joint research enterprise of the University of Maryland, College Park, the University of Maryland, Baltimore, and the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
IBBR leverages state-of-art integrative methods for bioanalytical, biophysical and structural characterization of biomolecules: cryo-electron microscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance, x-ray crystallography, small angle neutron and x-ray scattering and mass spectrometry.
IBBR researchers seek to advance therapeutic development, biomanufacturing, and state-of-the-art measurement technologies, to support accelerated delivery of safe and effective medicines to the public.
IBBR is a major initiative and supported in part by the University of Maryland Strategic Partnership: MPowering the State (MPower) , an initiative designed to achieve innovation and impact through collaboration.
Connecting
IBBR Commons
Sophisticated state-of-the-art instrumentation and facilities, and in-house expertise located in shared space and dedicated to advance research, support collaboration and foster innovation of methods. Instrumentation and facilities include tools for high-resolution structural biology, bioanalytical and biophysical measurement, protein engineering and cell culture, advanced computation including artificial intelligence and deep learning methods, and general laboratory services. These capabilities and advanced training are available to IBBR scientists and collaborators.
IBBR Postdoc Program
The IBBR Postdoc Program (IPP) focuses on collaborative research involving basic science and technology development that advances therapeutic development, vaccine development, and biomanufacturing. IPP Fellow project teams are designed with a combination of the IPP Fellow career goals and priorities of project mentors who can be from academic, government, and/or industrial laboratories throughout the University of Maryland, NIST and the I-270 corridor.
NMRPipe
IBBR is home to NMRPipe, a popular collection of programs and scripts for manipulating multidimensional Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) data. The use of NMRPipe is noted in roughly 40% of all NMR structures accepted into the Protein Data Bank.

Upcoming Events
Seminar: "Ethics, Standards, and Forensic DNA Typing"
Kelly Elkins
Towson University
Tuesday, April 22, 2025 - 11:00am
NIST Group Meeting; Karndeep Singh
Wednesday, April 23, 2025 - 11:00am
Research in Progress Seminar: Tom Cleveland
Monday, April 28, 2025 - 11:00am
Recent Publications
Recommended nomenclature convention for the NISTCHO cell line and its product monoclonal antibody, cNISTmAb.
NISTCHO is a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line expressing the same amino acid sequences as the heavy and light chains of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) monoclonal...
Citrus phloem specific transcriptional profiling through the development of a citrus tristeza virus expressed translating ribosome affinity purification system.
BACKGROUND
The analysis of translationally active mRNAs, or translatome, is a useful approach for monitoring cellular and plant physiological responses. One such method is the translating...
Critical Assessment of RNA and DNA Structure Predictions via Artificial Intelligence: The Imitation Game.
Computational predictions of biomolecular structure via artificial intelligence (AI) based approaches, as exemplified by AlphaFold software, have the potential to model of all life's biomolecules....